
When a browser requests a webpage, the server returns the response with an HTTP status code. Regardless of whether the server fulfills your request, the server will always return a status code to indicate the response was successful. If the server fails to return a response, the status code will indicate why it failed. The HTTP Status Code is returned as a part of the HTTP response header from the web server.
The are various reasons why a server may fail to return a valid response. Understanding HTTP status codes will help webmaster and developers help diagnose the problem, and minimize the downtime. An HTTP Status Code is a 3-digit number, and there are 5 groups of responses. The status codes are classified into 5 groups, and they are named after the 1st digit (i.e. 1XX, 2XX, 3XX, 4XX and 5XX).
Web Browsers generally do not show Status Codes as they are part of the header response, and not the display contents. Some CMS (Content Management Systems) and custom templates are used to display HTTP status codes like the one shown by Cloudflare below. Also, some developer tools allow programmers to display status codes when deemed necessary.
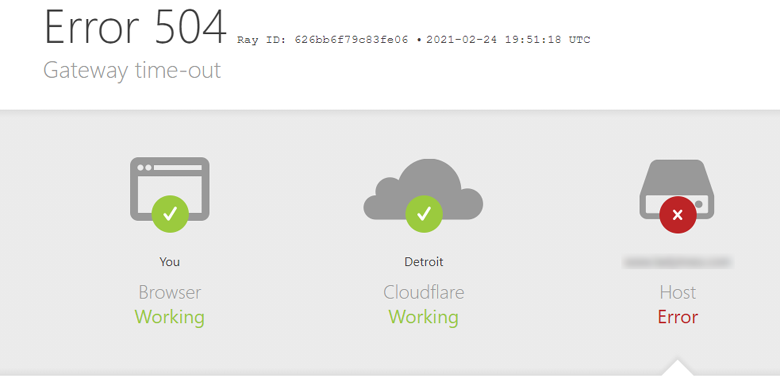
An example of Status Code 504 from CloudFlare
HTTP Status Code Classes
The status codes are grouped into 5 categories, each group indicates a general status. By just knowing the status class, you'll have a general idea of what may have gone wrong.
- 1XX: Informantional. The server received and understood the requests, and the request is being processed.
- 2XX: Successful. The server received, understood, and accepted the request.
- 3XX: Redirection. The server received a request, but the request was redirected to another page.
- 4XX: Client Errors. The server received a request, but there is a problem with the request.
- 5XX: Server Errors. The server received a request, but there is a problem on the server to fulfill the request.
Within each class, there are a variety of specific status codes that further clarify the response. The status codes in the 100-299, and 300-level are indicating the site is working as intended. The status codes from 400-599 are indicating that there are problems. You may use Google Search Console to diagnose your site performance.
A complete HTTP Status Codes
It is important for developers and SEO professionals to understand the HTTP status codes, and remedy any issues you may have on your website. Here is a complete list of HTTP Status codes with most commons highlighted in yellow:
1×× Informational
100 Continue
101 Switching Protocols
102 Processing
2×× Success
200 OK - This is the most common status code indicating the request was successfully carried out, and the response has been returned.
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
3×× Redirection
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently - A common way to permanently redirect a page to another page.
302 Moved Temporarily - A common way to temporarily redirect a page to another page.
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
4×× Client Error
400 Bad Request
401 Unauthorized
402 Payment Required
403 Forbidden - This indicates that the client doesn't have the authority to view this page.
404 Not Found - The requested page does not exist on the server.
405 Method Not Allowed
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
410 Gone
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I'm a teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
499 Client Closed Request
5×× Server Error
500 Internal Server Error - The server encountered a problem while processing a request. This is a generally programming error on the dynamic website.
501 Not Implemented
502 Bad Gateway
503 Service Unavailable - The server is overloaded with too many requests, and cannot fulfill this request. This may indicate the server may be under DDoS attack.
504 Gateway Timeout - If you're behind a reverse proxy such as Incapsula and CloudFlare, the network gateway closed the HTTP connection because there was no response from the server within the allotted time.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
506 Variant Also Negotiates
507 Insufficient Storage
508 Loop Detected
510 Not Extended
511 Network Authentication Required
599 Network Connect Timeout Error
Conclusion
For every HTTP request, the server responds with an HTTP response and accompanying headers. The HTTP response header includes the HTTP Status Code, and this indicates the status of the response. This is invaluable information used by developers and SEO professionals to understand the overall state of the website and also to troubleshoot issues when a problem arises.
If you wish to determine the status code of a webpage, you may use our HTTP Status Code Checker online tool to test up to 25 URLs at a time.
Share this post
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated. Spammy and bot submitted comments are deleted. Please submit the comments that are helpful to others, and we'll approve your comments. A comment that includes outbound link will only be approved if the content is relevant to the topic, and has some value to our readers.

Comments (0)
No comment