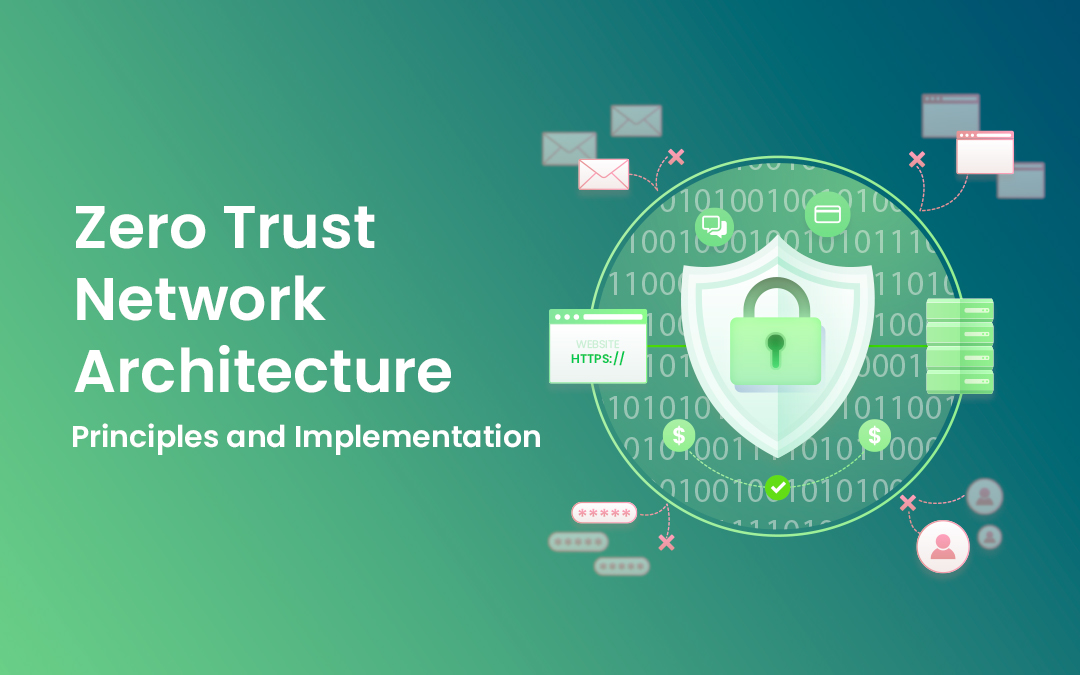
In today's rapidly evolving threat landscape, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient to protect modern distributed networks and cloud environments.

In today's rapidly evolving threat landscape, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient to protect modern distributed networks and cloud environments.

If you are looking to buy cat6 ethernet cables, you are going to have to choose from the two options: Cat6 plenum cable and riser. These are two different variants of the same bulk ethernet cable. The outer-jacket of these cables is designed for specific uses that make them different.
As organizations continue to migrate to cloud environments, the focus on securing these platforms has intensified. While significant attention is often given to controlling inbound traffic to protect against external threats, the importance of managing outbound or egress traffic is frequently underestimated. Egress traffic control is a critical component of cloud security, essential for protecting sensitive data, ensuring compliance, and optimizing operational costs.

Today, streaming has become a cornerstone of entertainment, with services like Netflix, Stan, Disney+, and Amazon Prime Video offering a plethora of content at our fingertips. However, having a reliable and fast internet connection is crucial to enjoy these services fully.

Cybersecurity risks can manifest in forms ranging from phishing attempts to advanced ransomware attacks. Therefore it is crucial to have solutions, like Network Detection and Response (NDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR). While these terms are occasionally used interchangeably they fulfill different roles.

In today's digital age, the stability and security of your internet connection are paramount. Whether you’re working from home, streaming videos, or managing sensitive data, a stable and secure connection ensures a seamless online experience and protects your personal information. This article delves into the factors affecting internet stability and security, and provides actionable tips to enhance both.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have evolved beyond mere buzzwords in today’s tech-driven landscape. These technologies are revolutionizing industries and transforming network management and optimization. By ensuring smooth internet connectivity and safeguarding against cyber threats, AI and ML have become essential components of modern network services. Let’s explore how these advancements are reshaping network management, managed network services, and intranet performance.
Since the invention of mobile phones in 1973, they have slowly dominated every part of our lives. From staying in touch with family and friends to keeping us connected at work, even when we can’t make it to the office, mobile phones have changed how we live.

The internet is an absolute necessity that powers up the digital world. It lets you work remotely, conduct video calls, play online games and stream all your favorite shows buffer-free.

Planning an event is like orchestrating a symphony, where every piece must be perfectly tuned, especially the internet. For event organizers and exhibitors aged 35-50, internet service at events is a make-or-break element.